
Dr. Widya Rosita, a faculty member at the Department of Nuclear Engineering and Engineering Physics, and team members published their research at the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering in 2020. The paper is titled “Sequential particle-size and magnetic separation for enrichment of rare-earth elements and yttrium in Indonesia coal fly ash.”
The demand for rare-earth elements and yttrium is higher than ever nowadays and keeps expanding. The annual demand doubled to 125,000 tonnes in 15 years and will reach 315,000 by 2030. The increasing demand for advanced electronics, semiconductors, and renewable technologies creates a soaring demand for rare-earth elements and yttrium (REY). However, the supply and availability of these elements become a problem. Previous research has shown that coal fly ash, resulting from the coal power plant combustion, contains a significant amount of REY, hence creating an opportunity for a recycling process. Due to its non-volatility, the distribution pattern of REY in fly ash will be identical to its distribution pattern in coal.
Coal fly ash is a coal combustion product driven out of coal-fired boilers. Fly ash consisted of particulates (fine coal particles as burned fuel). In the coal-fired power plant, fly ash is captured by electric precipitators or other filtration systems before being released into the environment. Nowadays, fly ash is used as an added mixture in the cement industry and to make geopolymer. Rare-earth elements and yttrium content at the coal fly ash are not currently treated to be recovered. Indonesian coal fly ash is claimed to have 38% REY contents with heavy distribution pattern. Dr. Widya Rosita and the team’s research is on how to treat and recover REY content from Indonesia coal fly ash [1]. Before it is feasible to recover, enrichment should be done to obtain higher content of REY.
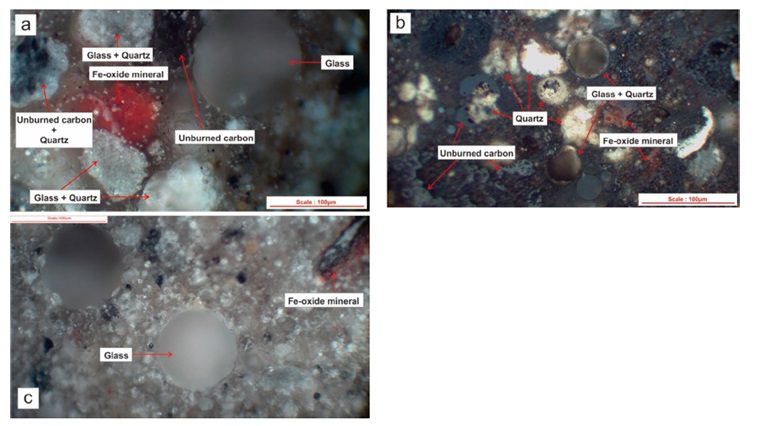
Figure 1. Observed contents of Indonesia coal fly ash from Tuban, Indramayu, and Paiton-1 coal-fired power plant [1]
The study’s coal fly ash is from Tuban, Indramayu, and Paiton-1 coal-fired power plant. The feedstock coal is from Kalimantan and South Sumatra. The separation consisted of physical separation (sieving) and magnetic separation. Both processes are done to enrich the REY content of the ash. The sieving process resulted in a 58.69% REY recovery factor with a 1.1 enrichment factor [1]. Then, the magnetic separation process separates the magnetic and nonmagnetic fractions. Based on the result, the nonmagnetic fraction contained more REY with a 91.64% separation factor [1]. The sequential processes achieved an overall 71.21% separation factor with a 1.23 enrichment factor.

Figure 2. Oxide contents after the separation process [1]
The paper proposed a new way to treat and recover rare-earth elements and yttrium (REY) from the Indonesian coal fly ash. Further development of this research can be beneficial in obtaining REY for advanced electronics and green technologies by utilizing the coal fly ash. This research can be accessed at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343719306980 . For questions and potential collaboration discussion, you can directly reach the author at:
Dr. Widya Rosita, Departemen Teknik Nuklir Teknik Fisika, Universitas Gadjah Mada
Jl. Grafika No.2, Sinduadi, Mlati, Sleman, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, 55281
Indonesia
Email: widyar@ugm.ac.id
(ayp)
Reference
- Rosita, Widya, I. Made Bendiyasa, Indra Perdana, and Ferian Anggara. “Sequential particle-size and magnetic separation for enrichment of rare-earth elements and yttrium in Indonesia coal fly ash.” Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 8, no. 1 (2020): 103575.



